India is ramping up efforts to reduce its dependency on Chinese raw materials, a strategic move that the government describes as being on a “war footing.” This shift comes amid growing geopolitical tensions and a global push for supply chain diversification. The Indian government is actively pursuing alternative sources and enhancing domestic production capabilities to mitigate risks associated with over-reliance on a single country.
According to industry experts, China currently supplies a significant portion of India’s raw materials, particularly in sectors such as electronics, pharmaceuticals, and automotive manufacturing. This dependency has raised concerns about economic vulnerability, especially in light of recent disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and ongoing border tensions between the two nations.
Strategic Diversification Efforts
The Indian government has initiated several measures to address this issue, including incentivizing domestic production and exploring trade partnerships with other countries. The “Atmanirbhar Bharat” (Self-Reliant India) initiative is at the forefront of these efforts, aiming to boost local manufacturing and reduce import dependency.
Meanwhile, the government is also investing in infrastructure and technology to support industries that are heavily reliant on Chinese imports. These initiatives are expected to create a more resilient supply chain and foster innovation within the country.
Expert Opinions and Industry Insights
Industry analysts suggest that while reducing dependency on Chinese raw materials is a prudent move, it will require significant time and investment. “Diversifying supply chains is not an overnight process. It involves building new relationships, investing in technology, and sometimes, re-engineering entire production processes,” said Dr. Arjun Mehta, an economist specializing in international trade.
According to a report by the Confederation of Indian Industry, over 70% of Indian companies in key sectors rely on Chinese imports for their raw materials.
However, experts also warn that the transition could lead to short-term disruptions and increased costs for businesses. Companies may face challenges in finding suppliers that can match China’s scale and pricing advantages.
Historical Context and Global Trends
This strategic shift is not unique to India. Globally, countries are re-evaluating their supply chain dependencies in response to geopolitical shifts and the lessons learned from the pandemic. The European Union and the United States have also launched initiatives to strengthen domestic industries and reduce reliance on single-source suppliers.
Historically, India’s economic policies have evolved from import substitution in the 1960s and 70s to liberalization in the 1990s. The current focus on self-reliance marks another pivotal chapter in this ongoing narrative.
Looking Ahead: Implications and Opportunities
As India progresses with its diversification strategy, the implications for the global market could be significant. A successful transition could position India as a more competitive player in the global supply chain, potentially attracting foreign investment and fostering economic growth.
Furthermore, this move could encourage other countries to reassess their own dependencies, potentially leading to a more balanced and resilient global trade ecosystem. However, the path forward will require careful planning and collaboration between the government, industry stakeholders, and international partners.
In conclusion, India’s efforts to reduce its dependency on Chinese raw materials represent a strategic shift with far-reaching implications. As the nation embarks on this journey, the world will be closely watching its progress and the potential ripple effects on global trade dynamics.
About The Author
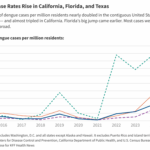 Surge in Dengue Cases Signals New Normal as Mosquito Season Peaks
Surge in Dengue Cases Signals New Normal as Mosquito Season Peaks GOP’s Unprecedented Move to Cut Medicaid Through Reconciliation
GOP’s Unprecedented Move to Cut Medicaid Through Reconciliation Funding Cuts Undermine Trump’s Health Agenda Despite MAHA Report Promises
Funding Cuts Undermine Trump’s Health Agenda Despite MAHA Report Promises New Fossil Discoveries Unravel the Mysteries of Earth’s “Great Dying”
New Fossil Discoveries Unravel the Mysteries of Earth’s “Great Dying” Understanding Cancer Screening: Key Insights and Recommendations
Understanding Cancer Screening: Key Insights and Recommendations