Health
New Study Reveals Potential Flaws in Heart Disease Testing Guidelines

Left main coronary artery (LMCA) disease, a condition that can lead to the infamous “widowmaker” heart attack, might be more prevalent than previously thought. A recent study published in the journal Circulation: Cardiovascular Interventions suggests that up to 28% of patients with this dangerous heart condition could be overlooked due to outdated clinical guidelines.
The research highlights a critical flaw in the current diagnostic approach, which relies on measuring blood pressure in the two branches of the left main coronary artery. Traditionally, doctors look for a uniform reduction in blood pressure across both branches. However, the study indicates that one branch often has lower blood pressure than the other, challenging the existing diagnostic criteria.
Understanding LMCA Disease
The left main coronary artery is the heart’s largest and most vital artery, supplying blood to a significant portion of the heart muscle. When narrowed by cholesterol build-up, it can lead to a severe heart attack. Currently, doctors diagnose LMCA disease by inserting a thin wire through the wrist to measure blood pressure in the two branches: the left anterior descending (LAD) artery and the left circumflex artery (LCx).
According to existing guidelines, a blood pressure score below 0.8 in these branches is considered significant, prompting immediate treatment. However, if one branch shows a score above 0.8, doctors might dismiss the presence of LMCA disease, potentially missing cases where the other branch indicates a problem.
New Findings and Their Implications
The study, conducted on 80 patients, found that conflicting blood pressure results between the two branches are not uncommon. Among these patients, 47 had a confirmed diagnosis of LMCA disease. The LAD, which supplies more of the heart muscle, may naturally have a lower blood pressure, suggesting that the current guidelines might need revision.
“These findings are so important because they will guide doctors to accurately interpret seemingly conflicting test results when assessing the LMCA,” said Professor Divaka Perera, a cardiology expert at King’s College.
The researchers argue that the guidelines should be updated to prevent overlooking cases of LMCA disease. They recommend that doctors should not solely rely on uniform blood pressure scores but consider the individual characteristics of each branch.
Expert Opinions and Future Directions
Dr. Ozan Demir, the study’s first author, emphasizes the need for further investigations when faced with conflicting test results. He suggests using advanced techniques like ultrasound or near-infrared cameras to visualize the artery’s interior for a more accurate diagnosis.
“A correct diagnosis is a crucial step in getting the right treatment for people with LMCA disease, which could prevent a major heart attack,” said Professor Bryan Williams, highlighting the importance of the study’s findings.
While the study provides valuable insights, the researchers acknowledge the need for larger studies to confirm their results. They urge the medical community to remain cautious and consider additional diagnostic methods until more evidence is available.
Looking Ahead
The potential revision of guidelines could significantly impact the diagnosis and treatment of LMCA disease, reducing the risk of missed cases and improving patient outcomes. As the medical field continues to evolve, adapting to new research findings is crucial for advancing patient care.
In the meantime, healthcare professionals are encouraged to apply a more nuanced approach to interpreting test results, ensuring that no case of LMCA disease goes undetected. The ongoing research in this area promises to refine diagnostic strategies and enhance the effectiveness of treatments for heart disease.
 Eko Health’s AI Heart Detection Gains CMS Approval, Boosting Access
Eko Health’s AI Heart Detection Gains CMS Approval, Boosting Access White House Adviser Confident in Passing Trump’s Tax Bill Amid Economic Concerns
White House Adviser Confident in Passing Trump’s Tax Bill Amid Economic Concerns Are Plastics in Your Kitchen a Hidden Health Hazard?
Are Plastics in Your Kitchen a Hidden Health Hazard? Mediterranean Marine Heat Wave Fuels Record-Breaking European Heat
Mediterranean Marine Heat Wave Fuels Record-Breaking European Heat Crypto’s Evolving Role in ETFs: Expert Insights and Market Dynamics
Crypto’s Evolving Role in ETFs: Expert Insights and Market Dynamics
Health
Genetically Modified Virus Shows Promise in Melanoma Treatment

The herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1), typically known for causing oral herpes, has shown potential as a treatment for advanced melanoma, a severe form of skin cancer. Results from a phase 1-2 clinical trial, presented by Keck Medicine of USC at the 2025 American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting, indicate that a genetically engineered version of the virus could significantly aid patients whose melanoma has not responded to traditional therapies.
The study, published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, involved 140 patients from the IGNYTE clinical trial. These individuals had advanced melanoma that either did not respond to or had ceased responding to immunotherapy treatments. Participants received a combination of a genetically modified HSV-1, known as RP1, and the immunotherapy drug nivolumab. The results were encouraging, with one-third of participants experiencing a tumor reduction of at least 30%, while nearly one in six patients had their tumors completely disappear.
Gino Kim In, MD, a medical oncologist at Keck Medicine and principal investigator of the trial, noted the significance of these findings. “The survival rate of untreatable advanced melanoma is only a few years, so this new therapy offers hope to patients who may have run out of options to fight the cancer,” he stated.
Innovative Approach to Cancer Treatment
The genetically modified HSV-1 tested in the trial, known as RP1, is part of an innovative class of cancer treatments called oncolytic viruses. These viruses are designed to specifically target and destroy cancer cells while eliciting a broad anti-tumor immune response throughout the body. Importantly, RP1 does not lead to herpes infections in patients.
In January 2025, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration granted priority review status for RP1 in combination with nivolumab for patients with advanced melanoma who had not responded to previous treatments. The dual approach aims to enhance the efficacy of RP1 by utilizing nivolumab, which activates the body’s immune system to attack cancer cells.
During the trial, patients received RP1 and nivolumab every two weeks for up to eight cycles. Those who showed a positive response continued with nivolumab alone for up to 30 cycles, or two years. Researchers monitored both treated and untreated tumors, finding that the shrinkage of injected tumors correlated with similar outcomes in uninjected tumors. This suggests that RP1 may effectively target cancer cells throughout the body, not just at the site of injection.
Future of Oncolytic Virus Therapy
The results from this trial are particularly promising given that melanoma is the fifth most common cancer among adults, with approximately half of advanced cases being resistant to current immunotherapy options. Dr. In emphasized the broader implications of these findings, stating, “This result suggests that RP1 is effective in targeting cancer throughout the entire body and not just the injected tumor, which expands the potential effectiveness of the drug because some tumors may be more difficult or impossible to reach.”
The safety profile of RP1 was also favorable, with the treatment being well tolerated by participants. While it is still early to determine the long-term sustainability of these positive outcomes, Dr. In remains optimistic about the future of oncolytic virus therapy. “I believe that oncolytic viruses will open up an important new approach to fighting cancer in some patients in the near future,” he added.
Following the success of the phase 1-2 trial, researchers, including Dr. In, have initiated a phase 3 trial, named IGNYTE-3, which aims to validate their findings across a larger global population of over 400 participants. Keck Medicine will again serve as one of the trial sites, with Dr. In leading the efforts.
Patients interested in participating in the IGNYTE-3 trial can reach out to Sandy Tran at [email protected]. The trial is sponsored by Replimune, the manufacturer of RP1 and other oncolytic immunotherapies.
As advancements in cancer treatment continue to evolve, the potential of genetically modified viruses like RP1 highlights a promising frontier in the fight against advanced melanoma and possibly other forms of cancer.
Health
Study Reveals Increased Hearing Loss Among Diverse Australian Children

Research conducted by The University of Queensland highlights a significant disparity in hearing loss among children from culturally and linguistically diverse (CALD) families in Australia. The study analyzed data from 1,469 children aged 11-12 and found that those from CALD backgrounds experienced a 58 percent higher likelihood of hearing loss compared to their peers from ethnic majority backgrounds.
Factors contributing to this increased risk include the proficiency of parents in English and their duration of residency in Australia. Dumini de Silva, a PhD student and audiologist at UQ’s School of Health and Rehabilitation Sciences, noted that children whose primary caregivers were recent immigrants with lower English proficiency faced particularly elevated odds of hearing loss. Conversely, a longer residency in Australia appears to reduce these risks.
Barriers to Accessing Healthcare Services
The research identifies several barriers that may hinder access to hearing health services for CALD families. These include cultural beliefs, a lack of trust in healthcare systems, and limited availability of interpreting services at hearing clinics. The study suggests that targeted hearing screening programs should be implemented for school-aged children from recently migrated families to address these inequalities.
According to Professor Piers Dawes, senior author of the study, Australia boasts one of the world’s most diverse populations, with approximately 1 in 4 Australians coming from diverse cultural and linguistic backgrounds. He emphasized the urgent need to investigate inequalities in hearing health among these communities, stating, “It is essential to understand hearing inequalities and the factors that contribute to it.”
Future Research and Implications
The study utilized hearing test result data collected from the 2015 Child Health Checkpoint as part of the Longitudinal Study of Australian Children. It is important to note that children with Indigenous backgrounds were not included in this research.
Dumini de Silva indicated that further investigations into the causes of hearing loss are necessary. Such research could inform the development of effective prevention strategies and early intervention programs. She highlighted the potential for missed or delayed intervention to have lifelong consequences for children’s educational outcomes and quality of life.
“It is also important for CALD communities to understand how common hearing loss is among their children,” de Silva stated. “This understanding is essential in addressing the disproportionate impact of hearing loss and empowering parents and caregivers to make informed decisions regarding their children’s hearing health.”
The findings of this important study are published in the journal Ear and Hearing. For more detailed insights, refer to the publication: de Silva, D., et al. (2025). Hearing Loss in Children From Culturally and Linguistically Diverse Communities in Australia. Ear and Hearing. doi.org/10.1097/aud.0000000000001695.
Health
Innovative ‘Sponge’ Cancer Test to Launch in UK Pharmacies
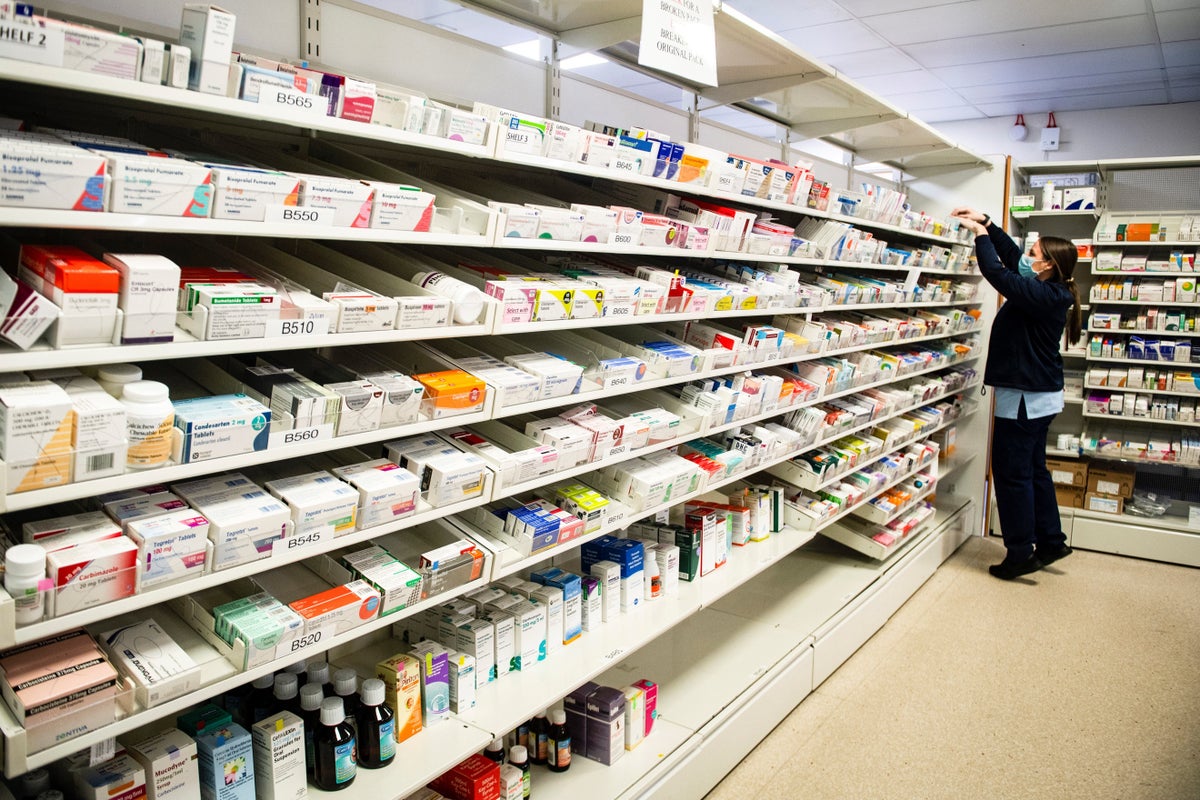

Hundreds of individuals suffering from persistent heartburn or acid reflux will soon have access to a revolutionary “sponge on a string” test at high-street pharmacies. This initiative, spearheaded by NHS England, aims to prevent oesophageal cancer by identifying individuals with Barrett’s oesophagus, a condition where stomach acid damages the oesophageal lining, potentially leading to cancer.
Starting early next year, approximately 1,500 people in London and the East Midlands will participate in these innovative “heartburn health checks.” During the test, patients swallow a small capsule attached to a string. Once in the stomach, the capsule dissolves, releasing a sponge about the size of a 1p coin. NHS staff then retrieve the sponge via the string, allowing it to collect cells from the oesophageal lining for laboratory analysis.
Revolutionizing Early Cancer Detection
This test, already in use in hospitals and community diagnostic centers, aims to reduce the need for invasive endoscopies. During the pilot, pharmacists will identify patients frequently purchasing over-the-counter heartburn medications who have not consulted a GP. The pilot is set to run for two years, with potential for broader implementation.
Professor Peter Johnson, NHS national cancer director, emphasized the convenience of the new pilot, stating, “This new pilot brings a convenient test to where people shop, making it easier than ever for patients to check signs and symptoms that might be worrying them.”
“For the majority of people with persistent reflux, these quick and easy heartburn health checks will provide peace of mind that you aren’t at increased risk of cancer,” Johnson added.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
If pre-cancerous cells are detected, treatments such as endoscopy or radiofrequency ablation can be administered. In the UK, nearly 10,000 patients are diagnosed with oesophageal cancer annually, with 80% diagnosed at a late stage. Early diagnosis is crucial, as only one in five people survive beyond a year.
Eddie, a 77-year-old from Suffolk, credits the test with potentially saving his life after years of persistent heartburn. “It used to wake me up at night, but I always thought it was just one of those things,” he shared. “To think that something as simple as swallowing a capsule could uncover a hidden risk is truly remarkable.”
“This test gave me peace of mind and access to early treatment and could mean the difference between life and death for so many others,” Eddie concluded.
Partnerships and Future Prospects
The NHS has partnered with Boots, diagnostics company Cyted Health, and Heartburn Cancer UK for this pilot. Public health minister Ashley Dalton highlighted the initiative as part of a broader 10-year health plan to provide convenient care closer to home.
“Today’s announcement is a fantastic example of the life-saving potential of healthcare on your high street,” Dalton remarked. “Being able to spot the warning signs using a 10-minute test in a local pharmacy – before cancer has even taken hold – will be a game-changer.”
“As part of our Plan for Change to tackle the biggest killers, this government is committed to back innovation and make our NHS fit for the future to drive up this country’s cancer survival rates,” Dalton affirmed.
As the pilot progresses, its success could pave the way for a nationwide rollout, potentially transforming the landscape of cancer prevention and early detection in the UK.
Health
Ballymena Police Seek Public’s Help in Identifying Suspect in Officer Attacks

Police in Ballymena have released two images of an individual they are keen to identify in connection with a series of disturbances and assaults on officers that have occurred since Monday, June 9. The images, which were disseminated to the public earlier today, are part of an ongoing investigation aimed at curbing the recent spate of violence in the area.
The Police Service of Northern Ireland (PSNI) is urging anyone who recognizes the person in the images to come forward. The appeal comes amid heightened tensions in Ballymena, where law enforcement has faced increasing challenges in maintaining order.
Background of the Investigation
The disturbances began earlier this month, with reports of disorderly conduct escalating into direct confrontations with police officers. According to authorities, these incidents have not only disrupted local peace but have also posed significant risks to public safety.
Chief Inspector John Smith, who is leading the investigation, emphasized the importance of community cooperation. “We are relying on the public to assist us in identifying this individual. Any information, no matter how small, could be crucial to our investigation,” he stated.
Community Impact and Response
The release of the images has sparked a mixed reaction within the Ballymena community. While some residents express concern over the safety of their neighborhood, others are hopeful that the identification of the suspect will lead to a swift resolution.
Local community leaders have called for calm and cooperation with the police. “It’s essential that we work together to restore peace and trust in our community,” said Marie O’Connor, a prominent figure in local civic groups.
Historical Context
This is not the first time Ballymena has experienced such unrest. Historically, the area has seen periodic spikes in violence, often linked to broader socio-political tensions in Northern Ireland. The current situation echoes past events where community and police relations were strained.
“The history of Northern Ireland is complex, and incidents like these remind us of the importance of dialogue and understanding,” remarked Dr. Ian McAllister, a historian specializing in Irish studies.
Steps Forward
As the investigation continues, the PSNI has increased patrols in key areas and is working closely with community organizations to address the underlying causes of the disorder. The police have also set up a dedicated hotline for tips related to the case.
Looking ahead, authorities are hopeful that the release of the images will lead to the identification of the suspect and help de-escalate the situation. “Our priority is to ensure the safety and security of all residents,” Chief Inspector Smith reiterated.
The situation in Ballymena remains fluid, with police urging vigilance and cooperation from the public. As the investigation unfolds, the community watches closely, hoping for a peaceful resolution to the unrest.
-

 Health4 days ago
Health4 days agoCrime Documentaries Gain Popularity Amid Summer Sports Frenzy
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoUK Couples Can Boost Tax-Free Allowance to £13,830 with Marriage Allowance
-
 Technology4 days ago
Technology4 days agoXbox Shelves Highly Anticipated Sci-Fi Game Blackbird Despite Praise
-

 Sports4 days ago
Sports4 days agoShane van Gisbergen’s Dominant Qualifying Run Sets Stage in Chicago
-

 Education12 hours ago
Education12 hours agoInside the Life of Nico Hülkenberg: Meet Eglė Ruškytė and Daughter Noemi
-

 Education14 hours ago
Education14 hours agoYasmin Broom: From X Factor Stardom to Love Island Fame
-

 Entertainment6 days ago
Entertainment6 days agoSlipknot’s Mysterious Countdown Sparks Speculation of Album Reissue
-

 Education4 days ago
Education4 days agoWigan School-Leavers Celebrate with Glamorous Prom Photos
-

 Top Stories10 hours ago
Top Stories10 hours agoIndiana Girl, 5, Seriously Injured in Pit Bull Attack Sparks Safety Debate
-

 Business11 hours ago
Business11 hours agoGemma Collins’ Weight-Loss Drug Ad Banned by UK Regulator
