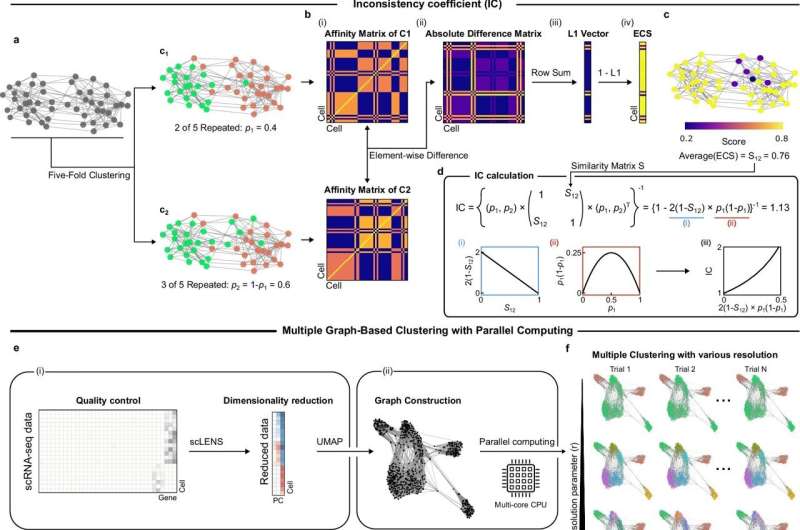
In a groundbreaking development, scientists from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) have introduced a novel tool designed to tackle the reliability crisis in single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq). The tool, named scICE (single-cell Inconsistency Clustering Estimator), promises to revolutionize the way researchers analyze gene expression at the single-cell level, a technique that has been pivotal in advancing fields such as immunology, oncology, and developmental biology.
Single-cell RNA sequencing has been a transformative technology, with over 40,000 studies utilizing it to explore the intricate diversity of cells within tissues and organisms. However, a persistent issue has plagued researchers: clustering instability. This problem arises when attempts to group cells based on expression patterns yield inconsistent results, even with repeated analyses of the same dataset. Such inaccuracies can lead to significant errors, like misclassifying normal cells as cancerous or overlooking rare but crucial cell types, thereby compromising therapeutic decisions.
Addressing the Clustering Instability Crisis
The introduction of scICE, developed under the leadership of Professor Kim Jae Kyoung, represents a significant advancement in addressing these challenges. Published in the journal Nature Communications, this new mathematical framework offers a more efficient and reliable method for assessing clustering stability in large-scale datasets.
Traditionally, researchers have relied on consensus methods, which involve repeatedly analyzing whether individual cell pairs are consistently classified into the same cluster. This process, while effective, is computationally intensive and impractical for datasets containing tens of thousands of cells. scICE circumvents this issue by employing a mathematically defined Inconsistency Coefficient (IC) to directly evaluate the stability of cell assignments, thus preserving only the most stable and biologically meaningful clusters.
Validation and Impact of scICE
Dr. Kim Hyun, the first author of the paper, elaborated on the tool’s significance:
“Reliability in single-cell clustering has long been overlooked. scICE opens a new path for quickly and easily verifying results.”
The research team validated scICE’s effectiveness by applying it to 48 real and simulated scRNA-seq datasets from various tissues, including the brain, lungs, and blood. Their findings revealed that approximately two-thirds of existing analyses were statistically unstable and unreliable. In contrast, scICE efficiently identified a small number of reliable results, significantly reducing the time and computational resources required while maintaining high accuracy.
Moreover, scICE has demonstrated an exceptional ability to detect rare cell types, often missed by conventional methods. In practice, it reliably identified rare immune cells through subclustering based on its framework, offering a new level of precision in data interpretation.
Broader Implications and Future Prospects
The implications of scICE extend beyond immediate research applications. By providing a means to mathematically validate clustering outcomes, scICE ensures higher confidence in conclusions drawn from single-cell data. This advancement is particularly crucial as the life sciences continue to rely heavily on precise data interpretation for developing new therapies and understanding complex biological processes.
Professor Kim Jae Kyoung expressed optimism about the tool’s future impact, stating,
“scICE will help researchers swiftly pursue follow-up studies based on reliable results. I hope it becomes a standard tool for trustworthy data interpretation across the life sciences.”
The research team has made scICE publicly available on GitHub, inviting the global scientific community to leverage its capabilities for enhanced data reliability.
As the life sciences field continues to evolve, tools like scICE are essential for overcoming current limitations and paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries. With its ability to deliver reliable and efficient clustering analysis, scICE is poised to become an indispensable asset in the toolkit of researchers worldwide.
For more information, refer to the study by Hyun Kim et al., titled “scICE: enhancing clustering reliability and efficiency of scRNA-seq data with multi-cluster label consistency evaluation,” published in Nature Communications. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-60702-8.